Utility methods for printing and formatting values
- Printing Values to String
- format.printValue - Prints any type of value to string
- format.DATE_FORMAT - Options for printValue Date Formats (see array.printValue(value, options))
- formatting Numbers
- format.zeroFill - Pads a number to a specific length
- format.divideR - Divides a number to provide { integer, remainder } - ex: 5/3 as ( 1, remainder 2 )
- format.compactNumber - Converts a number to a compact format, ex: 100K, 2M
- format.compactParse - Parses a compact number to a true number (very useful for sorting)
- Formatting Strings
- format.capitalize - Capitalizes only the first character in the string (ex: 'John paul');
- format.capitalizeAll - Capitalizes all the words in a string (ex: 'John Paul')
- format.ellipsify - Truncates a string if the length is 'too long'
- format.stripHtmlTags - removes html / xml tags from strings.
- format.limitLines(string, toLine, fromLine, lineSeparator) - selects only a subset of lines in a string
- format.consoleLines(...) - same as limit lines, only console.logs the string out.
- format.wordWrap(str, options) - breaks apart string by line length
- format.lineCount(str, options) - counts the number of lines in a string
- Replacing values in Strings
- format.replaceString(string, stringTupletsOrMap) - applies replace from a collection of [matcher, replacement] tuplets or map based on key-> values
- format.replaceStrings(stringsArray, stringTupletsOrMap) - applies replaceString on an array of values
- Formatting Time
- Mapping Values
- format.mapDomain - projects a value from a domain of expected values to a range of output values, ex: 10% of 2 Pi
- format.mapArrayDomain - projects a value from between a range a value, and picks the corresponding value from an array
- Identifying Time Periods
- format.timePeriod - Converts a time to a time period, very helpful for animations
- format.timePeriodPercent - Determines the percent complete of the current time period
- Converting values safely
- format.safeConvertString - converts a value to string, or uses a default for any error
- format.safeConvertFloat - converts a value to a Number (123.4), or uses a default for any error or NaN
- format.safeConvertInteger - converts a value to a Number (123), or uses a default for any error or NaN
- format.safeConvertBoolean - converts a value to a boolean
- Parsing values
- format.parseBoolean(val) - converts a value to a boolean value
- format.parseNumber(val, locale) - converts a value to a number
- Identifying values
- format.isEmptyValue - determine if a value is not 'empty'
- Extracting values
- format.extractWords - to extract the words from a string
- Making Printing Easier
- format.clearOutput - has the output cleared. Helpful for setting variables, or importing libraries.
Members
(static) DATE_FORMAT :DateFormat
- See:
Date Formats
Type:
Example
d = new Date();
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.LOCAL }; // .LOCAL = 'toLocaleString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//3/8/2022, 4:22:38 PM
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.LOCAL_DATE }; // .LOCAL_DATE = 'toLocaleDateString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//3/8/2022
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.LOCAL_TIME }; // .LOCAL_TIME = 'toLocaleTimeString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//4:22:38 PM
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.GMT }; // .GMT = 'toGMTString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//Tue, 08 Mar 2022 22:22:38 GMT
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.ISO }; // .ISO = 'toISOString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//2022-03-08T22:22:38.163Z
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.UTC }; // .UTC = 'toUTCString'
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//Tue, 08 Mar 2022 22:22:38 GMT
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.NONE };
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//Tue Mar 08 2022 16:22:38 GMT-0600 (Central Standard Time)Methods
(static) capitalize(str) → {String}
- See:
-
- capitalizeAll - to capitalize all words in a string
Capitalizes the first character of the string.
Example
utils.format.capitalize('john'); // 'John'
utils.format.capitalize('john doe'); // 'John doe'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
str |
String | String to capitalize the first letter only |
Returns:
- ex: 'John paul'
- Type
- String
(static) capitalizeAll(str) → {String}
- See:
-
- capitalizeAll - to capitalize all words in a string
Capitalizes all words in a string.
Example
utils.format.capitalizeAll('john'); // 'John'
utils.format.capitalizeAll('john doe'); // 'John Doe'
utils.format.capitalizeAll('john-paul'); // 'John-Paul'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
str |
String | String to capitalize |
Returns:
- ex: 'John-Paul'
- Type
- String
(static) clampDomain(value, domain) → {Number}
Clamps (restircts) a value to a specific domain.
Meaning if value is less than minimum, then the minimum is returned. If the value is greater than the maximum, then the maximum is returned.
NOTE: null or undefined are not treated specially when comparing to maximum or minimum values.
Example
format.clampDomain( -1, [0, 1]); // 0
format.clampDomain( 2, [0, 1]); // 1
format.clampDomain( 0.5, [0, 1]); // 0.5Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
value |
Number | the value that will be modified if less than min or max |
|||||||||
domain |
Array | Domain of min and max values Properties
|
Returns:
- minimum if value is less than minimum, maximum if more, value otherwise.
- Type
- Number
(static) compactNumber(num, digits) → {String}
- See:
-
- Number.toFixed(num, digits)
- Intl.NumberFormat() - as the compact format does something similar
Converts a number to a compact version.
| key | name | fullName | value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y | yotta | Septillion | 10^24 |
| Z | zetta | Sextillion | 10^21 |
| E | exa | Quintillion | 10^18 |
| P | peta | Quadrillion | 10^15 |
| T | tera | Trillion | 10^12 |
| G | giga | Billion | 10^9 |
| M | mega | Million | 10^6 |
| K | kilo | Thousand | 10^3 |
| m | milli | Thousandth | 0.001 |
| μ | micro | Millionth | 0.000001 |
| n | nano | Billionth | 10^-9 |
| p | pico | Trillionth | 10^-12 |
| f | femto | Quadrillionth | 10^-15 |
| a | atto | Quintillionth | 10^-18 |
| z | zepto | Sextillionth | 10^-21 |
| y | yocto | Septillionth | 10^-24 |
Note, a standard method Javascript is now available with Intl.NumberFormat()
This method handles very simple cases, but you can use the compact layout
for much more control.
Example
utils.format.compactNumber(123.456, 1); // 123.5
utils.format.compactNumber(759878, 0); // 760K
utils.format.compactNumber(0.0000002, 1); // 200n
//-- or using Intl.NumberFormat
new Intl.NumberFormat('en-GB', {
notation: "compact",
compactDisplay: "short"
}).format(987654321);
// → 988MParameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
num |
Number | Number to create into a compact number |
digits |
Number | Significant digits |
Returns:
- Type
- String
(static) compactParse(compactStr) → {Number}
This parses compact numbers, like 100K, 2M, etc.
| key | name | fullName | value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y | yotta | Septillion | 10^24 |
| Z | zetta | Sextillion | 10^21 |
| E | exa | Quintillion | 10^18 |
| P | peta | Quadrillion | 10^15 |
| T | tera | Trillion | 10^12 |
| G | giga | Billion | 10^9 |
| M | mega | Million | 10^6 |
| K | kilo | Thousand | 10^3 |
| m | milli | Thousandth | 0.001 |
| μ | micro | Millionth | 0.000001 |
| n | nano | Billionth | 10^-9 |
| p | pico | Trillionth | 10^-12 |
| f | femto | Quadrillionth | 10^-15 |
| a | atto | Quintillionth | 10^-18 |
| z | zepto | Sextillionth | 10^-21 |
| y | yocto | Septillionth | 10^-24 |
Example
utils.format.compactParse('1.2K'); // 1200
utils.format.compactParse('12'); // 12
utils.format.compactParse('299.8M')// 299800000Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
compactStr |
String | Compact Number String, like 100K, 2M, etc. |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
(static) consoleLines(str, toLine, fromLineopt, lineSeparatoropt) → {String}
- See:
Same as limitLines() - only prints to the console.
Example
str = '0\n1\n2\n3\n4\n5';
utils.format.consoleLines(str, 2);
// 1
// 2
//-- only lines from 2 to 4
utils.format.consoleLines(str, 4, 2);
// 2
// 3
//-- all lines after line 2
utils.format.consoleLines(str, undefined, 2);
//2
//3
//4
//5Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
str |
String | Object | string to be limited, or object to be json.stringify-ied |
||
toLine |
Number | |||
fromLine |
Number |
<optional> |
0
|
starting line number (starts at 0) |
lineSeparator |
String |
<optional> |
'\n'
|
separator for lines |
Returns:
- Type
- String
(static) constantFn(val) → {function}
A function that returns the value provided
alwaysBlack = utils.format.constantFn('#000000');
alwaysBlack(); // '#000000'
alwaysBlack(); // '#000000'
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | Any value |
Returns:
- a function that accepts no parameters, and always returns value provided
- Type
- function
(static) divideR(numerator, denominator) → {Object}
Divide a number and get the integer value and remainder
Example
utils.format.divideR(5, 3)
// ({ value: 1, remainder: 2 })Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
numerator |
Number | number to be divided |
denominator |
Number | number to divide with |
Returns:
- ({value, remainder})
- Type
- Object
(static) ellipsify(str, maxLenopt) → {String}
Ellipsifies a string (but only if it is longer than maxLen)
Example
utils.format.ellipsify('longName') // 'longName' (as maxLen is 50)
utils.format.ellipsify('longName', 8) // 'longName' (as maxLen is 8)
utils.format.ellipsify('longName', 4) // 'long…' (as str is longer than maxLen)Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
str |
String | string to be ellipsified |
||
maxLen |
Integer |
<optional> |
50
|
the maximum length of str before getting ellipsified |
Returns:
- Type
- String
(static) extractWords(strToExtractFrom, additionalNonBreakingCharacters) → {Array.<string>}
Identify an array of words each from a string.
Note that this uses the new Unicode Properties
using \p{L} to identify characters based on unicode properties.
For example:
strs = 'I am a Modern "major-general".';
utils.format.extractWords(strs);
// ['I', 'am', 'a', 'Modern', 'major', 'general'];
you can also include additional characters that will no longer be considered word boundaries.
strs = 'I am a Modern "major-general".';
utils.format.extractWords(strs, '-');
// ['I', 'am', 'a', 'Modern', 'major-general'];
arrays of strings are also supported
strs = ['letras mayúsculas de tamaño igual a las minúsculas',
'الاختراع، ومايكل هارت'];
utils.format.extractWords(strs);
// [ 'letras', 'mayúsculas', 'de', 'tamaño', 'igual', 'a', 'las', 'minúsculas', 'الاختراع', 'ومايكل', 'هارت'];
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
strToExtractFrom |
String | Array.<String> | collection of strings to extract words from |
additionalNonBreakingCharacters |
String | each char in this string will not be treated as a word boundry |
Returns:
- collection of words
- Type
- Array.<string>
(static) isEmptyValue(val) → {Boolean}
Tests for empty values:
- (zeros are allowed)
- not null
- not undefined
- not an empty string
- not an empty array
[]
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | a value to be tested |
Returns:
- TRUE if the value is not 'empty'
- Type
- Boolean
(static) limitLines(str, toLine, fromLineopt, lineSeparatoropt) → {String}
- See:
-
- format.consoleLines() - to console the values out
Narrows to only fromLine - toLine (inclusive) within a string.
Example
str = '0\n1\n2\n3\n4\n5';
utils.format.limitLines(str, 2); // '1\n2'
//-- only lines from 2 to 4
utils.format.limitLines(str, 4, 2); // '2\n3'
//-- all lines after line 2
utils.format.limitLines(str, undefined, 2); // '2\n3\n4\n5'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
str |
String | Object | string to be limited, or object to be json.stringify-ied |
||
toLine |
Number | |||
fromLine |
Number |
<optional> |
0
|
starting line number (starts at 0) |
lineSeparator |
String |
<optional> |
'\n'
|
separator for lines |
Returns:
- Type
- String
(static) lineCount(str, newlineCharacteropt) → {Number}
- See:
-
- wordWap(str, options)} for other options.
Determines the number of lines in a string
Example
utils.format.lineCount('single line'); // 1
utils.format.lineCount(`line 1
line 2
line 3`); // 3
utils.format.lineCount('line 1\rLine2\rLine3', '\r'); // 3Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
str |
String | String to be checked for number of lines |
||
newlineCharacter |
String |
<optional> |
'\n'
|
the newline character to use |
Returns:
- Number of lines found
- Type
- Number
(static) mapArrayDomain(val, targetArray, domain)
projects a value from a domain of expected values to an array - very useful for random distributions.
like mapping normal / gaussian distributions to an array of values with d3-random as format.mapArrayDomain projects a value from between a range a value, and picks the corresponding value from an array.
For example:
require('esm-hook');
d3 = require('d3');
utils = require('jupyter-ijavascript-utils');
//-- create a number generator using Normal / Gaussian distribution
randomGenerator = d3.randomNormal(
0.5, // mu - or centerline
0.1 // sigma - or spread of values
);
randomValue = randomGenerator();
// randomValue - 0.4
randomDataset = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'];
numPicks = 3; // increase to a larger number (ex: 1000) to better see distributions
//-- create an array of 3 items, each with the results from randomGenerator
results = utils.array.size(numPicks, () => randomGenerator());
// [ 0.6235937672428706, 0.4991359903898883, 0.4279365561645624 ]
//-- map those values to the randomDataset
resultPicks = results.map(val => ({ pick: utils.format.mapArrayDomain(val, randomDataset) }));
// [ { pick: 'g' }, { pick: 'e' }, { pick: 'e' } ]
//-- group them by the pick field
//-- then add a new property called count - using the # of records with the same value
groupedResults = utils.group.by(resultPicks, 'pick')
.reduce((list) => ({ count: list.length }));
// [ { pick: 'g', count: 1 }, { pick: 'e', count: 2 } ]
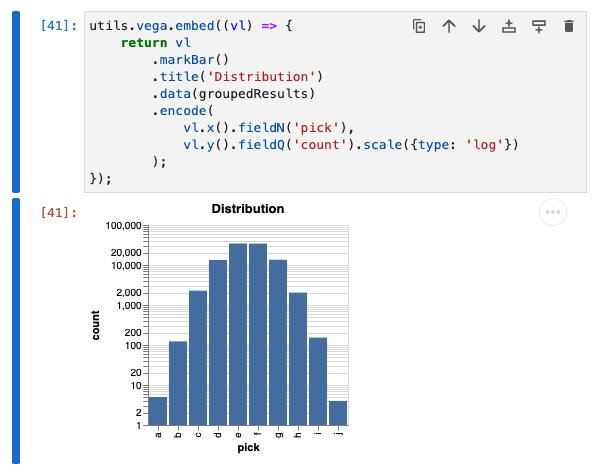
//-- make a bar chart (only with 10k results)
utils.vega.embed((vl) => {
return vl
.markBar()
.title('Distribution')
.data(groupedResults)
.encode(
vl.x().fieldN('pick'),
vl.y().fieldQ('count').scale({type: 'log'})
);
});
Example
//-- array of 10 values
randomArray = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(-1, randomArray, [0, 5]);
// 'a' - since it is below the minimum value
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(6, randomArray, [0, 5]);
// 'e' - since it is the minimum value
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(0.9, randomArray, [0, 5]);
// 'a'
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(1, randomArray, [0, 5]);
// 'b'
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(2.5, randomArray, [0, 5]);
// 'c'
//-- or leaving the domain of possible values value can be out:
utils.format.mapArrayDomain(0.5, randomArray); // assumed [0, 1]
// 'c'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
val |
Number | value to be mapped |
|||||||||||||||
targetArray |
Array | array of values to pick from |
|||||||||||||||
domain |
Array | [min, max] - domain of possible input values Properties
|
Returns:
Number
(static) mapDomain(val, domain, range)
projects a value from a domain of expected values to a range of output values, ex: 10% of 2 Pi.
This is SUPER helpful in normalizing values, or converting values from one "range" of values to another.
Example
utils.format.mapDomain(-2, [0, 10], [0, 1])
// 0 - since it is below the minimum value
utils.format.mapDomain(0, [0, 10], [0, 1])
// 0 - since it is the minimum value
utils.format.mapDomain(5, [0, 10], [0, 1])
// 0.5 - since it is 5/10
utils.format.mapDomain(12, [0, 10], [0, 1])
// 1 - since it is above the maximum value
utils.format.mapDomain(0.5, [0, 1], [0, 10])
// 5 - since it is half of 0-1, and half of 1-10
utils.format.mapDomain(0.5, [0, 1], [0, Math.PI + Math.PI])
// 3.1415 or Math.PI - since it is half of 2 PIParameters:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
val |
Number | value to be mapped |
|||||||||
domain |
Array | [min, max] - domain of possible input values Properties
|
|||||||||
range |
Array | [min, max] - range of values to map to Properties
|
Returns:
Number
(static) millisecondDuration(milliseconds) → {Duration}
Determines the length of time that a number of milliseconds take in duration
Example
d1 = new Date(Date.UTC(2022, 2, 8, 22, 55, 12));
// 2022-03-08T22:55:14.775Z
d2 = new Date(Date.UTC(2022, 2, 8, 23, 00, 0));
// 2022-03-08T23:02:18.040Z
utils.format.millisecondDuration(d2.getTime() - d1.getTime())
// {
// days: 0,
// hours: 0,
// minutes: 4,
// seconds: 48,
// milliseconds: 0,
// epoch: 288000
// }Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milliseconds |
Number | Number of millisecond duration |
Returns:
- Type
- Duration
(static) parseBoolean(val) → {Boolean}
Determines if a value is a boolean true value.
Matches for:
- boolean TRUE
- number 1
- string 'TRUE'
- string 'True'
- string 'true'
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | the value to be tested |
Returns:
- TRUE if the value matches
- Type
- Boolean
(static) parseNumber(val) → {Number}
Parses a given number, based on a Intl.NumberFormat
If the locale is not passed (ex: 'fr-FR'), then 'en-US' is assumed
Example
utils.format.parseNumber(10); // 10
utils.format.parseNumber('10'); // 10
utils.format.parseNumber('1,000'); // 1000
utils.format.parseNumber('1,000.5'); // 1000.5
utils.format.parseNumber('1,000', 'en-US'); // 1000
utils.format.parseNumber('1,000.5', 'en-US'); // 1000.5
utils.format.parseNumber('1 000', 'fr-FR'); // 1000
utils.format.parseNumber('1 000,5', 'fr-FR'); // 1000.5Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | value to parse |
Returns:
- parsed number
- Type
- Number
(static) printValue(value, options) → {string}
- See:
Print a value in legible string format
Note: collapsing
format = { dateFormat: utils.format.DATE_FORMAT.ISO };
utils.format.printValue( new Date(), format)
//2022-03-08T22:22:38.163Z
//-- but you will mostly be using this in aggregate, like with the TableGenerator
obj = { first: 'john', last: 'doe', classes: [23, 34], professor: { name: 'jane doe' }, dateTime: new Date(), aliases: new Set(['jdoe', 'j_doe'])}
new utils.TableGenerator([obj])
.generateMarkdown();
| first | last | classes | professor | dateTime | aliases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| john | doe | [23,34] | {"name":"jane doe"} | 2022-03-08T22:50:03.632Z | "Set("jdoe","j_doe")" |
new utils.TableGenerator([obj])
.printOptions({ collapse: true, dateFormat: 'toLocaleDateString' })
.generateMarkdown();
| first | last | classes | professor | dateTime | aliases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| john | doe | 23,34 | [object Object] | 3/8/2022 | [object Set] |
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
value |
any | the value to print |
|||||||||
options |
Object | collection of options Properties
|
Returns:
- legible formatted value
- Type
- string
(static) randomFloat(max, min) → {Number}
Generate a random Float between a maximum and minimum number
Example
utils.format.randomFloat(10) // 7.21323
utils.format.randomFloat(10) // 4.2232392Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
max |
Number | maximum value |
min |
Number | minimum value |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
(static) randomInt(max, min) → {Number}
Generate a random Integer between a maximum and a minimum number
Example
utils.format.randomInt(10) // 4
utils.format.randomInt(20, 10) // 11Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
max |
Number | maximum value |
min |
Number | minimum value |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
(static) replaceString(targetStr, stringTupletsOrMap) → {string}
Conveience function for calling format.replaceStrings - giving and receiving a single value (instead of an array of values).
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
targetStr |
String | A Single string to replace values on. |
stringTupletsOrMap |
Array | Map.<(string|RegExp), string> | [[search, replace]] or Map<String|RegExp,String> |
Returns:
- the targetStr with the values replaced
- Type
- string
(static) replaceStrings(targetStr, stringTupletsOrMap) → {Array.<string>}
- See:
-
- module:format.replaceStringsGlobal - to replace all instances
Performs a set of replacement against a string or list of strings.
The string replacements can either be [[search,replace],[search,replace]] or a map of Map([[search, replace], [search, replace]])
This is meant to provide a way to apply consistent string cleanups across projects.
example:
targetStrings = [
'jack and jill went up the hill',
'to fetch the pail of water',
'jack fell down and broke his crown',
'and jill came tumbling after'
];
//-- include an array of strings to all remove out
utils.format.replaceStrings(targetStrings, ['down ', ' of water']);
// [ 'jack and jill went up the hill',
// 'to fetch the pail',
// 'jack fell and broke his crown',
// 'and jill came tumbling after' ]
//-- or use tuplets of [find, replace] with regular expressions
//-- and strings not in tuplets are simply removed.
replaceValues = [['jack', 'john'], [/\s+jill/i, ' ringo'], ' down'];
utils.format.replaceStrings(targetStrings, replaceValues);
expected = [
'john and ringo went up the hill',
'to fetch the pail of water',
'john fell and broke his crown',
'and ringo came tumbling after'
];
//-- a map will do the same, but will not support regular expressions for keys
replaceValues = new Map();
replaceValues.set('jack', 'john');
replaceValues.set('jill', 'ringo');
utils.format.replaceStrings(targetStrings, replaceValues);
expected = [
'john and ringo went up the hill',
'to fetch the pail of water',
'john fell down and broke his crown',
'and ringo came tumbling after'
];
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
targetStr |
string | Array.<string> | the string to search for with the tuplets |
stringTupletsOrMap |
Array | Map.<(string|RegExp), string> | [[search, replace]] or Map<String|RegExp,String> |
Returns:
- the resulting list of strings
- Type
- Array.<string>
(static) safeConvertBoolean(val) → {Boolean}
Converts a value to boolean.
Note this uses the standard JavaScript truthy conversion,
but with special exceptions for strings: only 'true', 'yes', '1' are considered true.
Example
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean(1); // true
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean({ pojo: true }); // true
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('TruE'); // true - case insensitive
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('YeS'); // true - case insensitive
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('1'); // true
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean(0); // false
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean(null); // false
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('false'); // false
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('No'); // false
utils.format.safeConvertBoolean('0'); // falseParameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | value to be converted |
Returns:
- Type
- Boolean
(static) safeConvertFloat(val, otherwise) → {Number}
Converts a value to a Floating Number,
Or returns otherwise if any exceptions are found or value is NaN
Example
utils.format.safeConvertFloat('23.1'); // 23.1
utils.format.safeConvertFloat('not a number', -1); // -1Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | value to convert |
otherwise |
any | value to use if any exceptions are caught |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
(static) safeConvertInteger(val, otherwise, radixopt) → {Number}
Converts a value to a Floating Number,
Or returns otherwise if any exceptions are found or value is Not a Number.
Example
utils.format.safeConvertFloat('23'); // 23
utils.format.safeConvertFloat('not a number', -1); // -1Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
val |
any | value to convert |
||
otherwise |
any | value to use if any exceptions are caught |
||
radix |
Number |
<optional> |
10
|
radix to use in converting the string |
Returns:
- Type
- Number
(static) safeConvertString(val, otherwise) → {String|String}
- See:
Converts a value to a String,
Or returns otherwise if any exceptions are found.
Example
utils.format.safeConvertString(23); // '23'
const customObj = {
toString: () => `String Value`
};
utils.format.safeConvertString(customObj); // 'String Value'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
val |
any | value to convert |
otherwise |
any | value to use if any exceptions are caught |
Returns:
-
String(val)
- Type
- String
-
- Type
- String
(static) stripHtmlTags(str) → {String}
Strips any html or xml tags from a string.
Note, if you want to remove html entities (ex: or ‑), please consider other libraries
Example
utils.format.stripHtmlTags('Hello <br />Nice to see <b>you</b>'); // 'Hello Nice to see you'
utils.format.stripHtmlTags('example string'); // 'example string' -- untouchedParameters:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
str |
String | string to strip html / xml entities from |
Returns:
- Type
- String
(static) timePeriod(millisecondPeriod, timeMilliopt, startMilliopt) → {Number}
Given that a period of time is millisecondPeriod number of milliseconds long, determines which period of time we are currently in (timeEpoch / millisecondPeriod)
This is especially handy for animations or cyclical time measuring.
NOTE: consider sending the timeEpoch relative to a separate start time, it is rarely ever needed to know how many 10 second intervals occurred since 1970...
Likely, we care more that the animation should have cycled 40 times since the page loaded though.
Example
startTime = new Date(Date.UTC(2025, 01, 01, 9, 00));
nextTime = startTime;
// utils.format.timePeriod(1000)
// 164955061.3 - using the current time and epoch starting point
// - wait 3 seconds
nextTime = utils.date.add(startTime, { seconds: 3, milliseconds: 500 });
// 2025-02-01T09:00:03.500Z
utils.format.timePeriod(1000, nextTime, startTime);
// 3.5 - using the starting point instead
// - wait another 14 seconds
nextTime = utils.date.add(nextTime, { seconds: 14, milliseconds: 500 });
// 2025-02-01T09:00:18.000Z
utils.format.timePeriod(1000, nextTime, startTime);
// 18 - 1000 millisecond cycles elapsed
//-- same time period but divided by 5 second intervals
utils.format.timePeriod(5000, nextTime, startTime);
// 3.6 - 5000 millisecond cycles elapsedParameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
millisecondPeriod |
Integer | Number of Milliseconds in a Period of time |
||
timeMilli |
Integer |
<optional> |
now
|
optional time to check - in epoch milliseconds |
startMilli |
Integer |
<optional> |
null
|
optional starting epoch |
Returns:
- (timeEpoch - startEpoch) / millisecondPeriod - number of periods
- Type
- Number
(static) timePeriodPercent(millisecondPeriod, timeEpochopt) → {Number}
Given that a period of time is millisecondPeriod number of milliseconds long, determines how far along in the CURRENT PERIOD.
This is especially handy for animations or cyclical time measuring.
Example
startTime = new Date(Date.UTC(2025, 01, 01, 9, 0, 0, 0));
utils.format.timePeriodPercent(10000, startTime) // 0.0
//-- wait 14 seconds
nextTime = utils.date.add(startTime, { seconds: 14 });
// 2025-02-01T09:00:14.000Z
utils.format.timePeriodPercent(10000, nextTime) // 0.4
//-- wait 8 seconds
nextTime = utils.date.add(nextTime, { seconds: 8 });
// 2025-02-01T09:00:22.000Z
utils.format.timePeriodPercent(10000, nextTime) // 0.2Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
millisecondPeriod |
Integer | Number of Milliseconds in a Period of time |
||
timeEpoch |
Integer |
<optional> |
now
|
time to check - in epoch milliseconds |
Returns:
- percentage through the current millisecond period (0 <= x < 1)
- Type
- Number
(static) wordWrap(str, options) → {Array.<String>}
Breaks apart a string into an array of strings by a new line character.
Example
const str = 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor '
+ 'incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation';
//-- does not cut the line by default, and width of 50
utils.format.wordWrap(str);
// [
// 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing',
// 'elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore',
// 'et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam,',
// 'quis nostrud exercitation'
// ];
//-- you can also set the width, and whether to cut in the middle of the line
utils.format.wordWrap(str, { cut: true, width: 70 });
const expected = [
'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmo',
'd tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim',
'veniam, quis nostrud exercitation'
];Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
str |
String | string to be broken apart into lines |
||||||||||||||||||||
options |
Object | options to apply Properties
|
Returns:
- array of strings
- Type
- Array.<String>
(static) zeroFill(num, lenopt, fillopt) → {String}
- See:
-
- MDN - Pad Start - for padding strings at the start
- MDN - Pad End - for padding strings at the end
Print a number and zero fill it until it is len long.
Example
utils.format.zeroFill(23) // '023';
utils.format.zeroFill(23, 5) // '00023';
utils.format.zeroFill(23, 5, ' ') // ' 23'Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
num |
Number | Number to be converted |
||
len |
Number |
<optional> |
3
|
the length of the string |
fill |
String |
<optional> |
'0'
|
the value to pad with |
Returns:
- Type
- String
Type Definitions
Duration
Properties:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
days |
Number | |
hours |
Number | |
minutes |
Number | |
seconds |
Number | |
milliseconds |
Number | |
epoch |
Number | the total duration in milliseconds |
Type:
- Object